What are stains ? Types of staining.
What are stains?
-
Stains (or dyes) are chemical substances (usually organic salts) used in microbiology to impart color to microorganisms or cell components, making them visible under a microscope.
-
They help to highlight structures, differentiate organisms, and study morphology and physiology.

Principle of Staining
-
Most stains are salts with a colored ion (chromophore).
-
Depending on whether the cation (+) or anion (–) carries the color, stains are classified as:
-
Basic stains: positively charged chromophore (e.g., methylene blue, crystal violet, safranin). These bind to negatively charged cell components (like nucleic acids, cell walls).
-
Acidic stains: negatively charged chromophore (e.g., eosin, nigrosin). Cell surfaces repel these and stain the background (negative staining).
-
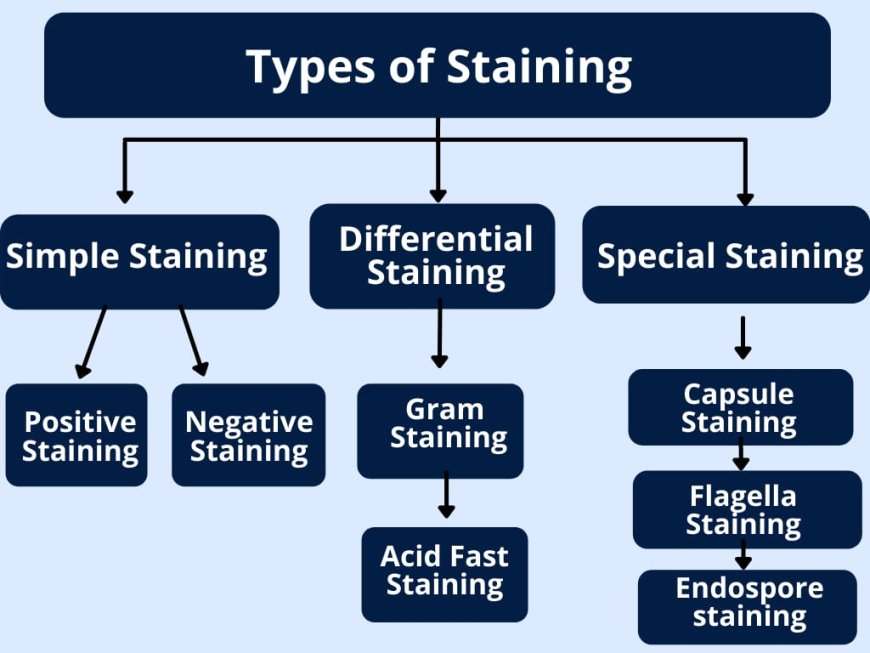
Types of Staining Techniques
A. Simple Staining
-
Uses a single dye (e.g., methylene blue, crystal violet).
-
Shows the size, shape, and arrangement of microorganisms.
B. Differential Staining
-
Uses two or more dyes to differentiate between types of microorganisms or cell structures.
-
Examples:
-
Gram staining differentiates bacteria into two categories: Gram-positive (purple) and Gram-negative (pink/red).
-
Acid-fast staining (Ziehl–Neelsen stain) – detects Mycobacterium spp. (acid-fast = red; non–acid-fast = blue).
-
C. Special (Structural) Staining
-
Highlights specific structures of microbes.
-
Examples:
-
Capsule stain – negative staining with India ink or nigrosin.
-
Spore stain (Schaeffer–Fulton method) – spores = green, vegetative cells = red/pink.
-
Flagella stain – makes flagella visible using special mordants.
-
D. Negative Staining
-
Uses acidic stains (e.g., nigrosin, India ink).
-
The background is stained while the cell remains colorless.
-
Useful for visualizing capsules and observing bacteria without the need for heat fixation.
In Short:
-
Stains = dyes that color microbes or their parts.
-
Types of staining =
-
Simple (one dye, morphology).
-
Differential (Gram, Acid-fast).
-
Special/Structural (spores, capsules, flagella).
-
Negative (background staining).
-
What's Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0