What is Human Skeleton an Overview
The human skeleton is a frame work of the body providing support protection and movement body .It consist of 206 bones .
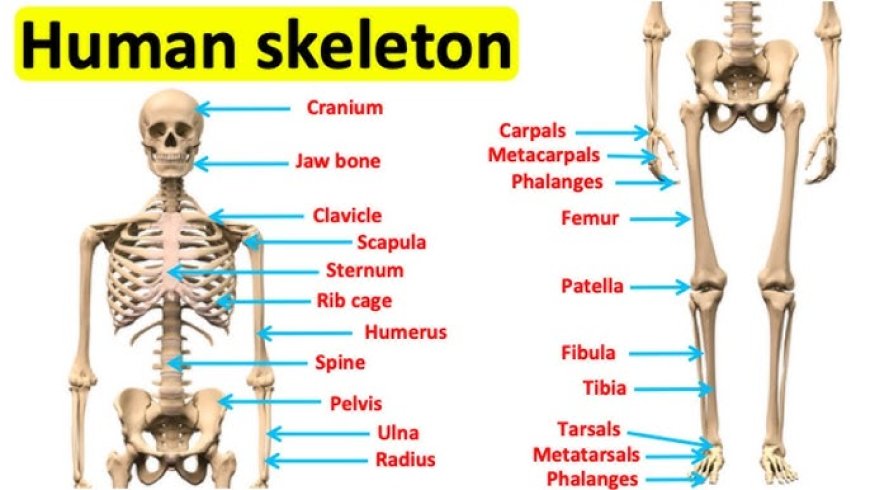
What is the Human Skeleton?
The human skeleton is the internal framework of the body made up of bones, joints, and cartilage. It gives shape to the body, supports organs, helps with movement, and protects vital structures like the brain, heart, and lungs.
Main Functions of the Skeleton
-
Support: Provides a rigid structure to support the body and keep its shape.
-
Protection: Shields important organs. For example:
-
Skull protects the brain.
-
Rib cage protects the heart and lungs.
-
-
Movement: Works with muscles to help the body move. Bones act like levers.
-
Blood Cell Production: Bone marrow inside some bones produces red and white blood cells.
-
Storage: Stores minerals like calcium and phosphorus, which are essential for body functions.
How Many Bones Are in the Human Body?
-
An adult human has 206 bones.
-
A newborn baby has about 300 bones, but some fuse together as the body grows.
Major Parts of the Skeleton
The skeleton is divided into two main parts:
1. Axial Skeleton (80 bones)
This forms the central part of the body.
-
Skull: Protects the brain.
-
Vertebral Column (Spine): Supports the body and protects the spinal cord. It has 33 vertebrae:
-
7 cervical (neck)
-
12 thoracic (chest)
-
5 lumbar (lower back)
-
5 fused sacral
-
4 fused coccygeal
-
-
Rib Cage: 12 pairs of ribs + sternum (breastbone); protects the heart and lungs.
2. Appendicular Skeleton (126 bones)
This includes limbs and the bones that connect them to the axial skeleton.
-
Pectoral Girdle: Shoulder bones (clavicle and scapula).
-
Upper Limbs: Arms, hands
-
Humerus (upper arm)
-
Radius and ulna (forearm)
-
Carpals, metacarpals, phalanges (wrist and fingers)
-
-
Pelvic Girdle: Hip bones.
-
Lower Limbs: Legs, feet
-
Femur (thigh bone – longest bone)
-
Patella (kneecap)
-
Tibia and fibula (lower leg)
-
Tarsals, metatarsals, phalanges (ankle and toes)
-
Types of Bones
-
Long Bones – Found in arms and legs (e.g., femur, humerus)
-
Short Bones – Small and cube-shaped (e.g., wrist bones)
-
Flat Bones – Thin and flat (e.g., skull, ribs)
-
Irregular Bones – Complex shapes (e.g., vertebrae)
-
Sesamoid Bones – Develop in tendons (e.g., patella)
Joints and Movement
-
Joints are where two or more bones meet.
-
They allow movement and flexibility.
-
Types of joints:
-
Fixed (Immovable) – Skull bones
-
Slightly Movable – Spine
-
Freely Movable (Synovial) – Most joints (e.g., knee, elbow)
-
Bone Health Tips
-
Eat foods rich in calcium and vitamin D.
-
Exercise regularly, especially weight-bearing activities.
-
Avoid smoking and limit alcohol.
-
Get regular checkups for bone density (especially in older adults).
Interesting Facts
-
The smallest bone is the stapes in the ear.
-
The largest bone is the femur in the thigh.
-
Bones are living tissues – they grow, repair, and renew themselves.
🌟 Conclusion
The human skeleton is more than just a collection of bones — it is a dynamic, living system that gives structure, enables movement, and supports life. Understanding its parts and functions helps us appreciate how our body works and how to take care of it.
What's Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0