ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF HUMAN EAR
DETAILED SIMPLE NOTES
INTRODUCTION
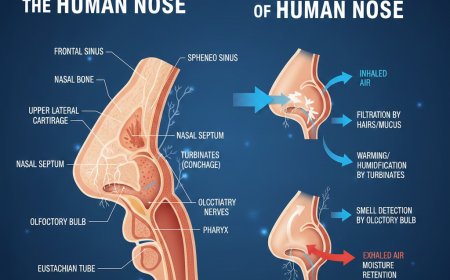
The ear is the organ of hearing and balance. It receives sound waves, converts them into nerve signals, and helps maintain body balance. The human ear is divided into three main parts
1. External ear
2. Middle ear
3. Inner ear
Each part has special structures that perform important functions in hearing and balance.
ANATOMY OF THE EAR
EXTERNAL EAR
The external ear consists of
Pinna or auricle
External auditory canal
Tympanic membrane or eardrum
Pinna
The visible part of the ear made of cartilage and skin. It collects sound waves from the environment and directs them into the ear canal.
External auditory canal
A tube about 2.5 cm long.
It carries sound waves from the pinna to the eardrum.
It contains glands that produce earwax. Earwax protects the ear from dust and insects.
Tympanic membrane
A thin, cone shaped membrane.
It vibrates when sound waves hit it.
It marks the boundary between the external and middle ear.
---
MIDDLE EAR
The middle ear is an air filled cavity located inside the temporal bone. It contains three tiny bones called ossicles and also has a tube called the eustachian tube.
Ossicles
These are the smallest bones in the human body. They transmit and amplify sound vibrations.
Malleus or hammer
Incus or anvil
Stapes or stirrup
Malleus
Attached to the tympanic membrane. It receives vibrations first.
Incus
Connects the malleus to the stapes.
Stapes
The smallest bone in the body. It connects to the oval window of the inner ear and passes vibrations into the inner ear.
Eustachian tube
A tube connecting the middle ear to the throat.
It helps maintain equal air pressure on both sides of the eardrum.
It opens during actions like swallowing and yawning.
INNER EAR
The inner ear is the most complex part. It contains two main structures
Cochlea
Vestibular apparatus
Cochlea
A spiral shaped, snail like structure.
It contains fluid filled chambers.
It has special sensory cells called hair cells.
These hair cells convert sound vibrations into electrical nerve impulses.
The auditory nerve carries these impulses to the brain.
Vestibular apparatus
This part controls balance and body position. It includes
Semicircular canals
Utricle
Saccule
Semicircular canals
Three curved tubes filled with fluid.
They detect rotational movements of the head.
Utricle and saccule
Detect linear movements like forward, backward, upward and downward movements.
They also help maintain posture and balance.
---
PHYSIOLOGY OF HEARING
Step 1
Sound waves enter the external ear through the pinna and ear canal.
Step 2
Waves strike the tympanic membrane and cause it to vibrate.
Step 3
These vibrations pass to the ossicles (malleus, incus, stapes).
The ossicles amplify and transmit the vibrations.
Step 4
Stapes pushes the oval window of the cochlea and creates fluid waves inside the cochlea.
Step 5
Fluid movement bends the hair cells inside the cochlea.
Bending of hair cells generates nerve impulses.
Step 6
These nerve impulses travel through the auditory nerve to the brain.
The brain interprets the signals as sound.
PHYSIOLOGY OF BALANCE
Semicircular canals detect rotational movements of the head.
The movement of fluid inside these canals stimulates sensory cells.
Utricle and saccule detect linear movement and position of the head.
These signals travel through the vestibular nerve to the brain.
The brain uses this information to maintain balance and coordination.
---
COMMON DISORDERS OF EAR
Otitis media
Infection of middle ear causing pain and fever.
Tinnitus
Ringing sound in the ear.
Vertigo
A feeling of spinning due to inner ear imbalance.
Hearing loss
May be conductive or sensorineural.
Conductive hearing loss occurs in the external or middle ear.
Sensorineural hearing loss occurs in the cochlea or auditory nerve.
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0