Structure of DNA Double Helix and RNA (Easy & Detailed Explanation)(FBISE recommended Topic)

Structure of DNA Double Helix and RNA (Very Easy & Detailed Explanation)
Introduction
DNA and RNA are very important molecules found in all living cells. They are called nucleic acids. DNA stores information, and RNA helps to use that information to make proteins. Without DNA and RNA, life is not possible.
What is DNA?
DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) is the genetic material of living organisms. It carries instructions for:
-
Body shape
-
Eye color
-
Growth
-
Cell activities
DNA is found mainly in the nucleus of the cell.
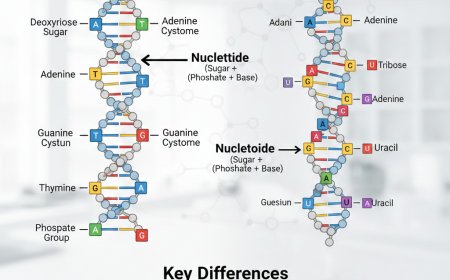
Basic Building Block of DNA (Very Easy)
DNA is made of many small units called nucleotides.
Each DNA nucleotide has THREE parts:
-
Phosphate group
-
Acts like a connector
-
-
Sugar (Deoxyribose)
-
Gives strength to DNA
-
-
Nitrogen base
-
Carries genetic code
-
Nitrogen Bases in DNA (Easy to Remember)
There are four bases in DNA:
-
A = Adenine
-
T = Thymine
-
G = Guanine
-
C = Cytosine
Double Helix Structure of DNA (Explained Very Simply)
DNA has a double helix shape.
What does Double Helix mean?
-
Double → Two strands
-
Helix → Twisted shape
So, DNA has two long strands twisted around each other, like a spiral staircase or a twisted ladder.
DNA Looks Like a Twisted Ladder
Parts of the DNA Ladder:
1. Sides of the ladder
-
Made of sugar and phosphate
-
Called the sugar-phosphate backbone
-
These sides are strong and protective
2. Steps (Rungs) of the ladder
-
Made of nitrogen bases
-
Bases join in pairs
Base Pairing Rule (Very Important)
DNA bases always pair in a fixed way:
-
A pairs with T
-
G pairs with C
This pairing is called complementary base pairing.
How are bases joined?
-
Bases are joined by hydrogen bonds
-
Hydrogen bonds are weak, so DNA can easily open during copying
Direction of DNA Strands (Easy Concept)
-
The two DNA strands run in opposite directions
-
This is called antiparallel arrangement
-
This helps in DNA replication
Why DNA Double Helix is Important?
The double helix structure:
-
Protects genetic information
-
Helps DNA to copy itself
-
Makes DNA stable and strong
-
Allows accurate transfer of traits from parents to children
Structure of RNA (Very Easy Explanation)
What is RNA?
RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) helps DNA in making proteins. Proteins are needed for:
-
Growth
-
Repair
-
Enzymes
-
Hormones
RNA is found in the nucleus and cytoplasm.
Components of RNA (Simple)
RNA is also made of nucleotides, but they are slightly different.
Each RNA nucleotide has:
-
Phosphate group
-
Ribose sugar
-
Nitrogen base
Nitrogen Bases in RNA
RNA has four bases, but one is different:
-
A = Adenine
-
U = Uracil
-
G = Guanine
-
C = Cytosine
⚠️ Thymine is NOT present in RNA
➡️ It is replaced by Uracil
Structure of RNA (Very Simple)
-
RNA is single-stranded
-
It does not form a double helix
-
It can fold into different shapes
-
RNA is shorter than DNA
Types of RNA (Easy Words)
1. mRNA (Messenger RNA)
-
Carries message from DNA
-
Takes instructions to ribosome
2. tRNA (Transfer RNA)
-
Brings amino acids
-
Helps build protein
3. rRNA (Ribosomal RNA)
-
Makes ribosomes
-
Ribosomes are protein factories
DNA vs RNA (Very Easy Table)
| Feature | DNA | RNA |
|---|---|---|
| Strands | Double | Single |
| Shape | Double helix | Simple strand |
| Sugar | Deoxyribose | Ribose |
| Base | Thymine | Uracil |
| Function | Stores info | Makes protein |
| Location | Nucleus | Nucleus & cytoplasm |
What's Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0