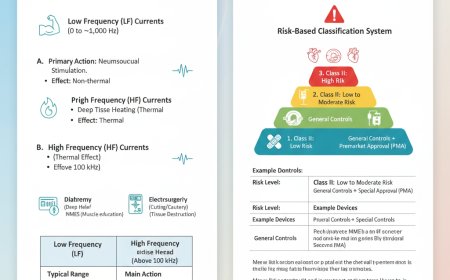
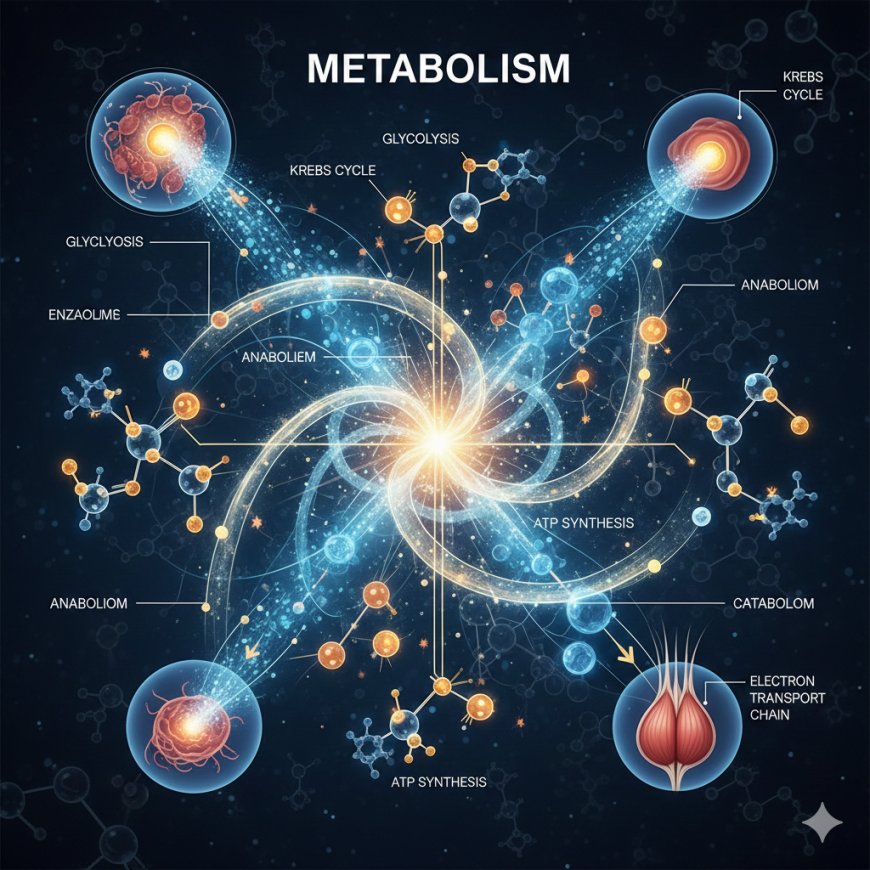
Metabolism means all the chemical reactions taking place inside the body to maintain life. Every activity in the body such as breathing, thinking, digestion, movement, repairing tissues and maintaining body temperature happens because of metabolism. Metabolism has two major parts. The first part is anabolism. Anabolism means building. In this process the body builds new tissues, stores nutrients, makes proteins, forms fats when extra food is available and repairs damaged cells. This process needs energy. The second part is catabolism. Catabolism means breaking. In this process the body breaks food molecules to release energy. Glucose, fats and proteins are broken down during catabolism. The energy released from catabolism is used to support anabolism and other body functions.
The main energy molecule of the body is ATP. ATP is like a battery that stores energy in a usable form. Whenever the body needs energy, ATP is used. ATP is required for muscle contraction, heart function, nerve signals, active transport like the sodium potassium pump, digestion, protein synthesis, and maintenance of body temperature. The body continuously makes ATP because ATP cannot be stored for long.
The body gets energy from three types of nutrients which are carbohydrates, fats and proteins. Carbohydrates are the body's first and fastest source of energy. Glucose is the main carbohydrate used by the cells. When glucose is more than needed, the body stores it as glycogen in the liver and muscles. When glucose is less, the body breaks glycogen to release glucose. Fats are the body's richest source of energy and provide more energy than carbohydrates. Fats are used during fasting, long exercise and starvation. Fats also help form cell membranes, hormones and protect organs. Proteins are mainly used for building the body. Muscles, enzymes, hormones, antibodies and many cellular structures are made of proteins. Proteins are used for energy only when carbohydrates and fats are not available.
There are several important metabolic pathways. Glycolysis is the first step in glucose breakdown. Glycolysis does not require oxygen. It takes place in the cytoplasm and produces a small amount of ATP. The next step is the Krebs cycle which happens in the mitochondria and requires oxygen. It produces more ATP and releases carbon dioxide. The last step is the electron transport chain which happens in the inner membrane of mitochondria. This step produces the maximum ATP in the entire process.
Carbohydrate metabolism includes storing glucose, releasing glucose and making glucose. When there is extra glucose, the body converts it into glycogen. This process is called glycogenesis. When blood glucose falls, glycogen is broken down to release glucose. This process is called glycogenolysis. If the body is in fasting or starvation and no glucose or glycogen is left, the body makes glucose from amino acids or fat parts. This process is called gluconeogenesis. Carbohydrate metabolism is controlled by hormones. Insulin lowers blood glucose by helping glucose enter cells and promoting storage. Glucagon raises blood glucose by breaking glycogen. Cortisol, adrenaline and growth hormone also help increase blood glucose during stress.
Fat metabolism includes fat breakdown and fat formation. Fat breakdown is called lipolysis. This happens during fasting, exercise or low carbohydrate intake. Fatty acids produced from fat breakdown enter the mitochondria and produce energy through beta oxidation. If the body is low on carbohydrates, the liver converts fatty acids into ketone bodies. This process is called ketogenesis. These ketones can be used by the brain and muscles for energy. When the body has extra carbohydrates, it converts them into fat. This process is called lipogenesis.
Protein metabolism involves digestion of proteins into amino acids, using amino acids for body building and removing nitrogen waste. Amino acids are used to make muscles, enzymes, hormones and immune proteins. Extra amino acids cannot be stored. The nitrogen part of amino acids is removed through a process called deamination. This nitrogen is converted to urea in the liver and excreted by the kidneys.
Basal metabolic rate or BMR means the minimum amount of energy the body needs to function at rest. BMR depends on several factors. Young people have higher BMR than older people. Males have higher BMR than females because of higher muscle mass. Thyroid hormones increase BMR. Fever increases BMR. Starvation and hypothyroidism decrease BMR.
Hormones play a major role in controlling metabolism. Insulin promotes storage and decreases blood sugar. Glucagon raises blood sugar during fasting. Thyroid hormones increase energy usage in the whole body. Cortisol increases glucose production during stress. Adrenaline increases fast energy production during emergencies.
The metabolism changes in fasting. During the first few hours the body uses stored glucose. After six to twelve hours the stored glycogen begins to decrease and fat breakdown begins. After one day the liver forms ketones which provide energy to the brain and other organs. The body tries to protect muscle tissue by using mainly fat and ketones.
There are some metabolic disorders. Diabetes occurs when the body does not use insulin properly or does not make enough insulin. This causes high blood glucose. Hyperthyroidism causes fast metabolism, weight loss and heat intolerance. Hypothyroidism causes slow metabolism, weight gain and cold intolerance. Obesity occurs when the body stores too much fat because of extra food intake and less activity.
Understanding metabolism helps medical students understand diseases like diabetes, thyroid disorders, starvation, obesity, fever, fluid and nutrition management and how energy is produced in cells. It also helps in understanding how medicines like insulin, steroids and thyroid drugs work.
 Like
5
Like
5
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0